As per the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), the top countries contributing to FDI equity inflows into India until March 31st, 2025 were Mauritius (25%), Singapore (24%), the USA (10%), the Netherlands (7%), and Japan (6%).
The share of FDI equity inflows by top investing countries in FY 2024-25 was as follows:
- Mauritius: US$8,344 million
- Singapore: US$14,942 million
- USA: US$5,457 million
- Netherlands: US$4,620 million
- Japan: US$2,478 million
Additionally, the top five sectors attracting the highest FDI equity inflows in India were:
- Services sector (16%) – finance, banking, insurance, outsourcing, research and development, and technology testing
- Computer software and hardware (15%)
- Trading (7%)
- Telecommunications (5%)
- Automobile industry (5%)
| Sector | Opportunities | Worth (US$) |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | 107 | 37.72 mn |
| BFSI | 127 | 1.89 mn |
| Electricity Generation | 646 | 341.44 bn |
| CSR | 802 | 33.82 bn |
| Defense | 9 | 555.78 mn |
| IT/ITES | 127 | 1.37 bn |
| Logistics Infrastructure | 81 | 5.51 bn |
| Food Processing & Agriculture | 400 | 14.33 bn |
| Retail and E-Commerce | 197 | 0.38 mn |
| Electronics Manufacturing | 580 | 522.96 mn |
| Food Processing | 31 | 2.42 bn |
| Telecommunication | 85 | 37.67 bn |
| Tourism, Hospitality & Wellness | 268 | 9.49 bn |
| Pharma, Biotech & Lifesciences | 91 | 129.45 mn |
| Real Estate | 1096 | 250.46 bn |
| Urban Public Transport | 228 | 103.49 bn |
| Energy Storage | 114 | 35.32 bn |
| Education | 825 | 30.33 bn |
| Railways | 908 | 268.93 bn |
| Healthcare | 1147 | 31.74 bn |
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is subject to limitations in certain sectors, with varying degrees of government regulation:
- Petroleum refining (by Public Sector Undertakings - PSUs): Up to 49 percent FDI is permitted under the automatic route.
- Broadcasting content services: This includes terrestrial FM radio broadcasting, where 49 percent FDI is allowed through the government route.
- Digital media: Foreign investment is restricted to 26 percent and requires approval through the government route.
- Multi-brand retail trading: FDI is permitted up to 51 percent, subject to government approval.
- Print media: Publishing of newspapers, periodicals, and Indian editions of foreign magazines covering news and current affairs allows 26 percent FDI under the government route.
- Duty-free shops: 100 percent FDI is allowed under the automatic route for shops located and operated within customs bonded areas.
Certain sectors are entirely closed to foreign investment, including:
- Lottery business: This includes government and private lotteries, online lotteries, and related activities.
- Chit funds: Investment in chit fund companies is not permitted.
- Trading in Transferable Development Rights (TDR): Foreign investment in TDR trading is restricted.
- Tobacco products: Manufacturing of cigars, cheroots, cigarillos, and cigarettes (including those made from tobacco or substitutes) is prohibited.
- Gambling and betting: This includes casinos and other forms of betting activities.
- Nidhi companies: These non-banking financial institutions are not open to foreign investment.
- Real estate business and farmhouse construction: FDI is not permitted in real estate development for speculative purposes or construction of farmhouses. However, this restriction does not apply to township development, residential or commercial construction, infrastructure projects (such as roads and bridges), or Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) regulated under SEBI (REITs) Regulations, 2014.
- Sectors reserved for government control: FDI is not allowed in atomic energy and certain railway operations, except for specific activities permitted under the Consolidated FDI Policy.
Additionally, foreign technology collaboration, including franchising, trademark licensing, brand name agreements, and management contracts, is strictly prohibited for both lottery businesses and gambling and betting activities.

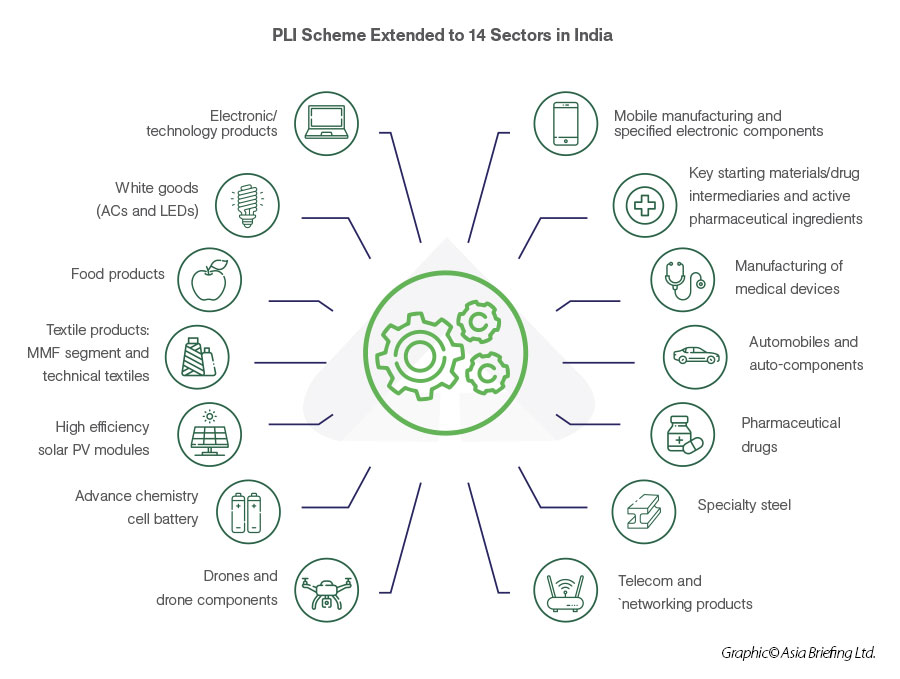
Developing India as a global manufacturing hub
To develop India into a global manufacturing hub and speed up job creation, the government has rolled out PLI schemes in 14 sectors since 2020, with incentives amounting to INR 1.97 trillion (US$23.81 billion).
The government is offering large incentives to foreign players to cover critical gaps in the domestic manufacturing capacity in these identified sectors.

Major startup sectors in India


Sector insights guides
FAQ:Logistics Sector in India and Opportunities for Foreign Investors
Can you give a brief overview of India’s logistics sector?
Logistics sector in India is a US$ 200 billion market, growing at a CAGR of 10.5 percent. India has the 2nd largest road network in the world and around 60-65 percent of transport takes place by road. National highways account for 2 percent of the total road network and carry over 40 percent of total traffic. India has a well-developed framework for Public-Private-Partnerships (PPP) in the highway sector. The government’s initiatives including big thrust on highways build up, Make in India, dedicated freight and industrial corridors, among others have potentially redefined the logistics sector in India.
What are the incentives provided by the government for road and highway sector?
Some of the incentives provided by the government include:
- 100 percent FDI through automatic route
- Duty free import of modern high capacity construction equipment
- Capital grant up to 40 percent of project cost to enhance viability on a case to case basis
Can you list the key government infrastructure programs?
- Industrial Corridors for industrial activity with planned greenfield industrial investment cities
- Dedicated Freight Corridors, high speed and high-capacity railway corridors dedicated for freight movement
- Bharatmala, a pan-India programme for the highways sector that focuses on optimizing efficiency of freight and passenger movement by bridging critical infrastructure gaps through development of Economic Corridors, Inter Corridors and Feeder Routes, National Corridor Efficiency Improvement, Border and International connectivity roads, Coastal and Port connectivity roads and Green-field expressways.
- Sagarmala Programme which focuses on port modernization, port connectivity, port-led industrialization, and coastal community development
- Logistics Efficiency Enhancement Program (LEEP), under which Multi-Modal Logistics Parks are being developed to enhance freight transportation and reduce time and cost.
What are the opportunities for foreign investors in the logistics sector?
- The roads and highways market is expected to record a CAGR of around 36 percent during 2016-2025
- India has the world’s largest railway network in terms of passenger traffic. The government has proposed to redevelop around 123 railway stations with world-class facilities.
- Under the Sagarmala Programme, US$ 123 billion would be invested for port modernization and connectivity
- Policy support and the government’s massive push to infrastructure is expected to create more opportunities for investors. The government has allocated around US$ 1.4 trillion for infrastructure to be invested until 2025.