Corporate tax is levied on the income earned by companies at a rate varying between 22-40 percent, depending on the companies’ particulars.
A company, whether Indian or foreign, is liable to pay CIT under the country’s Income Tax Act, 1961.
Domestic corporations are registered under the Indian Companies Act and have their business and management entirely based in India. On the other hand, foreign corporations are companies that are not registered under the Indian Companies Act and have their base and management outside India.
Foreign corporations are liable for corporate taxes in India only on the income earned within the country. However, domestic corporations are taxed on their overall income.
CIT rate
India’s corporate tax structure offers varied tax rates tailored to company size and legal entity type, reinforcing the objective to foster a competitive investment climate. Business structures—ranging from domestic companies to wholly owned subsidiaries and LLPs—are taxed differently based on their form and functional objectives.
| Business Structure | Tax Rate (approx.) | Repatriation Flexibility | Key Tax Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wholly-Owned Subsidiary (WOS) | 22% (with surcharges), MAT applicable | Dividend subject to withholding tax | Eligible for treaty benefits, lower tax rate under certain schemes |
| Branch Office | 40% (including surcharge and cess) | Repatriation allowed, taxed at branch level | Limited scope, higher tax outgo |
| Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) | 30% (plus surcharge and cess) | Profit distribution tax-exempt | No DDT, however, may face scrutiny on repatriation arrangements |
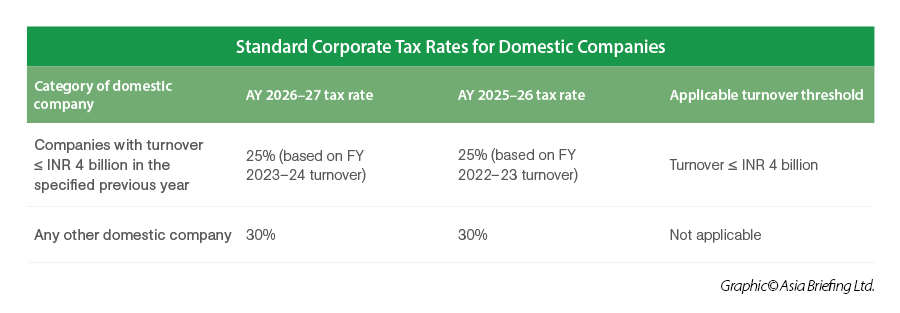
Tax rate for domestic companies
.jpg)
.jpg)
Corporate residence
A company is treated as a resident of India in any previous year if:
- It is an Indian company, or
- Its place of effective management in that year is in India.
Tax rates for foreign companies
A foreign company is liable to pay income tax at 35 percent of the average taxable Income.
| Income | Turnover ≤ INR 4 billion in FY 2020/21 | Other Domestic Companies | Foreign Companies with Permanent Establishment in India | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | Effective* | Basic | Effective* | Basic | Effective* | |
| Less than INR 10 million | 25% | 26 | 30% | 31.2 | 35% | 36.4 |
| More than INR 10 million but < INR 100 million | 25% | 27.82 | 30% | 33.38 | 35% | 37.13 |
| More than INR 100 million | 25% | 29.12 | 30% | 34.94 | 35% | 38.22 |
| Note: Effective tax rates include surcharge and health and education cess. For resident companies, surcharge is 0%, 7%, or 12% depending on income. For non-resident companies, it is 0%, 2%, or 5%, based on income. Health and education cess is levied at 4%. | ||||||
Tax rate for partnership firms, including LLP or local authorities
A partnership firm, LLP, or a local authority must pay income tax at 30 percent of average taxable Income.
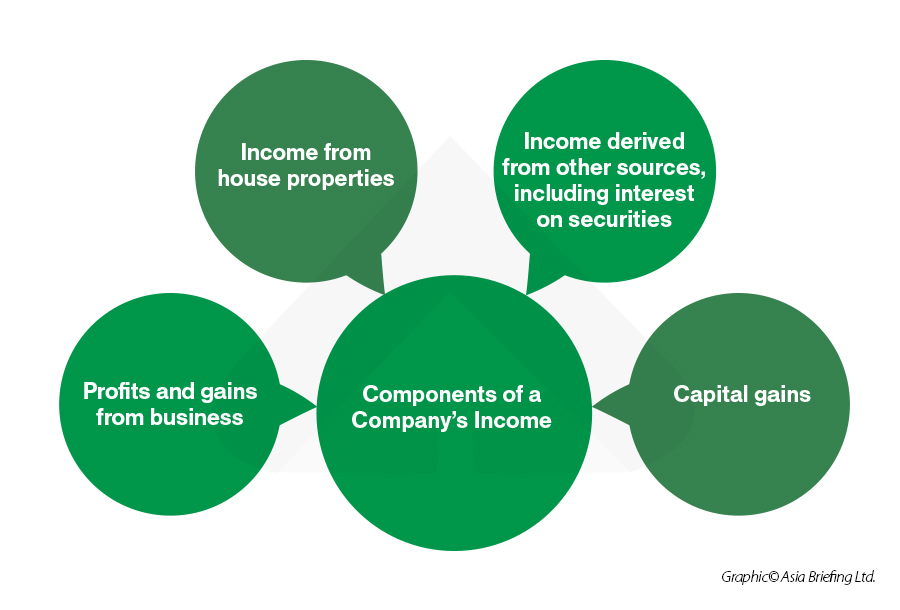
Components of taxable corporate income in India
Corporate tax in India is calculated after taking into account deductions such as depreciation, administrative expenses, cost of goods sold, and salary expenses. Both domestic and foreign corporations in India must pay corporate tax, which is based on the corporate income tax rate and their annual turnover.
Lowered corporate tax rate for eligible companies
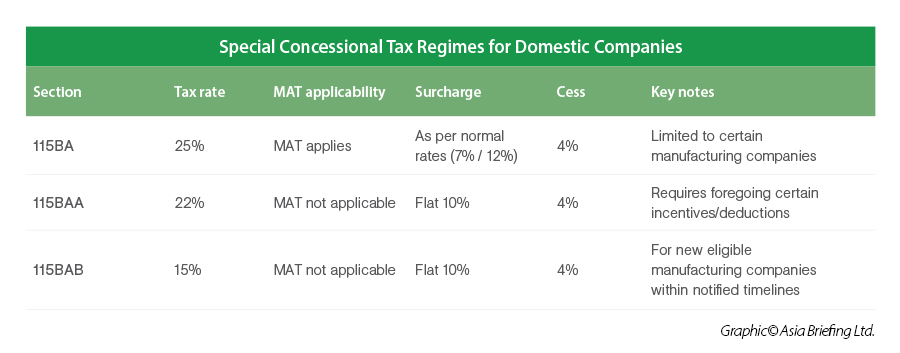
The corporate tax rate for domestic (locally incorporated) companies is 22 percent. Choosing the concessional regime would require meeting certain specified conditions.
Increase in threshold limits of presumptive taxation scheme for professionals/ businesses
Starting from the assessment year (AY) 2025-26, subject to certain conditions, the threshold limit for Section 44AD has increased to INR 3,00,00,000, while the limit for Section 44ADA has increased to INR 75,00,000.
If a non-resident chooses to be taxed in a particular year, they will not be permitted to offset any unabsorbed depreciation or carry forward losses in subsequent years. These changes will be effective from the assessment year (AY) 2024-25 and onward.
Corporate tax comparison: India vs. major global destinations
India has taken significant steps in recent years to boost its appeal as a competitive tax jurisdiction. One of the key reforms includes the introduction of a concessional corporate tax rate of 22 percent for domestic companies that meet certain eligibility criteria. This move aims to reduce the tax burden and simplify compliance. For companies that do not opt for this concessional scheme, the standard corporate tax rates remain at 25 or 30 percent, depending on their annual turnover.
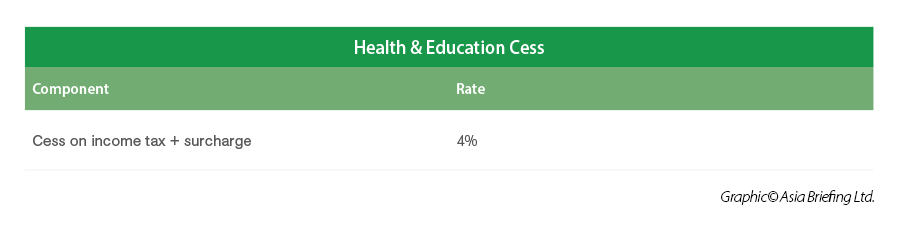
When surcharges and health and education cess are factored in, the effective tax rate under the concessional regime comes to approximately 25.17 percent. Additionally, India enforces a Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT) at a rate of 15 percent of book profits to ensure that companies with low taxable income still contribute to the tax base. It's also important to note that dividends are now taxed in the hands of shareholders, following the abolition of the Dividend Distribution Tax (DDT).
When compared globally, India’s corporate tax rates align with those of several major economies:
- In the United States, the federal corporate tax rate stands at 21 percent. When state taxes are included, the effective tax rate ranges from 25 to 28 percent. Dividends distributed to shareholders are subject to separate taxation, including withholding tax for foreign investors.
- Across the European Union, rates differ by country. Germany’s effective corporate tax rate is around 30 percent due to added trade taxes and surcharges. France applies a flat rate of 25 percent, while the Netherlands uses a tiered model—19 percent on income up to €200,000 and 25.8 percent on income above that threshold. Most EU countries also impose dividend withholding taxes, which vary by jurisdiction.
- In ASEAN nations, corporate tax policies are generally more investor-friendly. Singapore leads with a low headline rate of 17 percent, often further reduced by various incentives. Malaysia taxes companies at 24 percent, Thailand at 20 percent, and Indonesia at 22 percent, with a roadmap to bring that down to 20 percent. Many of these countries also offer sector-specific tax holidays and incentive schemes.
- In China, the corporate tax rate is set at 25 percent. However, high-tech enterprises operating in designated development zones enjoy a reduced rate of 15 percent. The country promotes innovation and regional development through targeted tax incentives. Dividends paid to foreign shareholders are generally subject to a 10 percent withholding tax.
| Country | Tax Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Argentina | 35 |
| Australia | 30 |
| Brazil | 34 |
| Canada | 26.5 |
| China | 25 |
| France | 25 |
| Germany | 30 |
| India | 34.94 |
| Indonesia | 22 |
| Italy | 24 |
| Japan | 30.62 |
| Mexico | 30 |
| *Netherlands | 25.8 |
| Saudi Arabia | 20 |
| **South Africa | 27 |
| South Korea | 24 |
| ***Spain | 25 |
| Turkey | 25 |
| United Kingdom | 25 |
| United States | 21 |
|
Notes:
|
|
India's key direct and indirect tax components affecting foreign businesses
Corporate Income Tax and Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT)
India offers a multi-tiered corporate tax framework. While domestic companies can opt for concessional tax rates, the system also includes a Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT), which ensures companies with low or no taxable income still pay a baseline tax.
- MAT is generally charged at 15 percent of book profits, plus applicable surcharges and cess.
- Units located in International Financial Services Centres (IFSCs) and earning exclusively in foreign currency benefit from a lower MAT rate of 9 percent.
- Companies choosing special tax regimes under Sections 115BAA and 115BAB are exempt from MAT but must forgo various deductions (with limited exceptions such as under Sections 80JJAA and 80M).
India’s system emphasizes digital compliance, with mandatory electronic filing, strict transfer pricing rules, and anti-avoidance measures to curb tax evasion.
Dividend taxation and withholding for foreign shareholders
India abolished the Dividend Distribution Tax (DDT) in FY 2020-21. Now, the tax liability on dividends has shifted to shareholders. Foreign investors are typically subject to a 20 percent withholding tax on dividends, although this can be reduced under applicable Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAAs).
To benefit from lower treaty rates, investors must submit:
- A Tax Residency Certificate (TRC)
- Form 10F
- A declaration of beneficial ownership
Without these, higher tax rates apply, though any excess withholding may be claimed upon filing a return.
India’s GST framework and cross-border compliance
India's Goods and Services Tax (GST) replaced a maze of state and central levies with a unified system. For domestic businesses, GST has simplified tax compliance. However, foreign companies must navigate added layers of complexity, especially in cross-border transactions:
- Imports of goods/services are subject to Integrated GST (IGST), which can be claimed as input credit.
- Non-resident service providers, particularly those offering digital services (e.g., streaming, SaaS, online advertising), must register under the OIDAR (Online Information and Database Access or Retrieval) regime or as Non-Resident Taxable Persons (NRTPs).
- Compliance with input credit rules, refund procedures, and tax registration is crucial.
Capital gains tax and foreign investment
Foreign investors in India are liable to pay capital gains tax on the transfer of capital assets, including shares and property. The rate depends on the type of asset and the holding period:
- Listed securities (held ≤12 months): Short-term gains taxed at 15 percent
- Listed securities (held >12 months): Long-term gains taxed at 12.5 percent on gains above INR 100,000 (without indexation)
- Unlisted assets: Short-term gains taxed at 30 percent, while long-term gains may be taxed at 10–12.5 percent, subject to treaty conditions
A 20 percent TDS typically applies to non-residents, subject to DTAA relief. To claim treaty benefits, detailed documentation must be provided; otherwise, the default higher rate is applied.
Interest, royalty, and technical service fees paid to non-residents are also subject to withholding tax, ranging from 10 percent to 20 percent, again depending on treaty provisions.
Tax implications of mergers and acquisitions
Foreign investors engaging in mergers, acquisitions, or business reorganizations must account for a range of tax obligations:
- Capital gains tax, stamp duty, and indirect taxes may apply based on deal structure (asset vs. share purchase).
- Certain domestic amalgamations and demergers are tax-neutral under Indian law, provided they meet specified conditions.
- Cross-border deals, however, must comply with Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) regulations and may trigger transfer pricing and withholding obligations.
India’s digital tax reforms
India continues aligning its tax regime with global standards:
- In 2025, the Equalization Levy on digital services was repealed, ending a 2 percent levy on e-commerce platforms and a 6 percent levy on digital advertising. This simplifies taxation for foreign digital service providers and signals a more investor-friendly approach.
- Meanwhile, foreign firms offering digital content, SaaS, and subscriptions must still comply with OIDAR GST obligations—including registration, invoicing, and remittance on B2C transactions.
Global Minimum Tax and its implications for India
India is expected to evaluate its participation in the OECD’s global minimum tax framework under Pillar Two, which sets a 15 percent minimum effective tax rate on large multinationals.
If implemented, Indian subsidiaries of global corporations—or foreign firms with a significant presence in India—could face additional tax liabilities if they benefit from low-tax jurisdictions. Businesses may need to restructure operations, revisit transfer pricing policies, and reassess repatriation strategies.
Compliance and filing requirements
Foreign companies operating in India must adhere to clearly defined tax filing obligations. Here’s a breakdown of essential compliance milestones:
- Permanent Account Number (PAN): Must be obtained before beginning operations.
- Annual Income Tax Return (Form ITR-6): Due by October 31 following the end of the financial year if the entity is subject to audit.
- Transfer Pricing Documentation (Form 3CEB): Required for entities engaged in international or specified domestic transactions, also due by October 31.
- Tax Audit Report (Form 3CD): Mandatory for entities exceeding prescribed turnover thresholds under Section 44AB of the Income Tax Act.
Additionally, companies must file quarterly TDS returns covering payments to both residents and non-residents. Failure to comply may result in penalties and interest under Sections 234A, 234B, and 234C, and can affect the ability to carry forward business losses or utilize MAT credits.
GST compliance
India’s Goods and Services Tax (GST) has unified indirect taxation but still demands careful, multi-step compliance—especially for foreign businesses.
Registration and filing
GST registration becomes mandatory once a business crosses the turnover threshold or engages in activities like interstate supply, e-commerce, or import of services. Once registered, businesses must:
- File monthly returns (GSTR-1 for outward supplies, GSTR-3B for tax payments)
- Submit annual filings (GSTR-9) and audited reconciliations (GSTR-9C) if turnover exceeds prescribed limits
E-Invoicing and Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM)
- E-invoicing is now mandatory for companies crossing certain turnover levels. Failure to comply can invalidate tax invoices and block input tax credits.
- Under RCM, businesses must pay GST on imports or transactions with unregistered vendors, and self-account the tax liability.
Major changes are rolling out to bolster transparency and combat fraud:
- Mandatory multi-factor authentication (MFA) for accessing the GST portal
- Tighter control over E-Way Bills to track goods movement more accurately
- New requirements around invoice series management, revised turnover thresholds, and updates to RCM compliance












